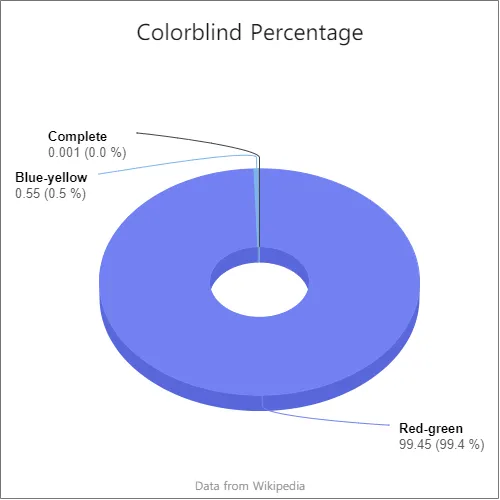
Red-Green color blindness has many subtypes. It is the most common form of color blindness, causing about 99% of all color vision problems. It occurs when the red and green receptors in the retina are not working correctly. The result is that reds and greens appear similar, resulting in a loss of detail.
Here is a complete guide on Red Green Colorblindness that will help you understand this condition better.
What Does Red Green Colorblind Means
Red-green color blindness is a condition. It restricts a person’s ability to tell red from green. There are four primary variants of this condition: Deuteranomaly, Deuteranopia, Protanomaly, and Protanopia.
This condition is often attributed to specific genes. It impedes the brain’s ability to see differences between red and green. As a result, people with this color blindness struggle to tell these two colors apart. They may also mistake other colors for red or green.
Numerous daily tasks can prove challenging for those with red-green colorblindness. Traffic signals can be a problem. For example, colorblind people see fire engines as black, not red. They also struggle to tell green and yellow lights apart.
Other tasks, like reading maps and identifying money, might also be hard. Recognizing blood in medical situations could be hard too.
Also, red-green colorblind people may struggle to tell apart more colors. For example, purple and blue, or yellow and green. This condition could also make it hard for them to tell fruit and vegetables apart. They might confuse red apples for green spinach, for instance.
What Are Types Of Red Green Colorblindness?
There are four types of red-green colorblindness:
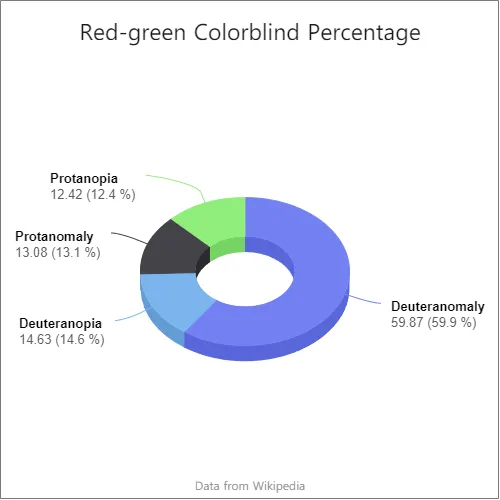
Deuteranomaly (weak green)
Deuteranomaly – People with this condition are less sensitive to green light than normal, but their ability to see red is usually unaffected.
About 6% of men and 0.4% of women have deuteranopia in the United States.
The word “deuteranomaly” comes from Greek. Deutero means second or double. And, anomalia means anomaly or abnormality. The name means that this type of color vision deficiency is caused by an abnormality in one of the cones in the retina. The cones are sensitive to green light but not red light.
Deuteranopia (green absence)
Deuteranopia is characterized by a lack of green cones, which are sensitive to wavelengths around 564 nm and 544 nm (green).
As a result, people with deuteranopia can only see shades of red and yellow. The absence of green hues makes it harder for them to distinguish between shades of red, orange, brown and yellow. Their blue and purple appear more similar than they do to people with normal vision.
More than 5% of the male population and less than 1% of the female population.
Protanomaly (weak red)
Protanomaly– People with protanomaly struggle to see reds that differ from yellow or brown. This is especially true at night or in low light. The word “protanomaly” means this, but for red light instead of green.
It is caused by a mutation in either the L or M opsin gene on chromosome 7. The gene codes for one of two pigments used to see short-wavelength light (blues).
About 1% of men and 0.02% of women have this condition.
Protanopia (red absence)
Protanopia is a complete loss of sensitivity to red light. People with this condition cannot tell the difference between colors like red and brown, pink and orange, or maroon and purple. The word “protanopia” comes from the Greek words “proto-” (before) and “-anoia” (seeing).
About 1% of men and 0.03% of women have this condition.
Signs And Symptoms
The term “red-green color blindness” is a bit misleading. The issue isn’t with red, green, or blue. It’s with how your brain sees them. Red-green color blindness affects the ability to tell red, orange, and yellow apart. It also affects telling greenish-yellow, yellow-green, and blue-green apart.
What Do Red Green Color Blind People See
You have difficulty distinguishing between red and green traffic lights;
You confuse similar shades of green when shopping for fruit;
You often mistake a Christmas tree ornament for a piece of broccoli;
You think that all brown objects look black.

Why Do People Have?
Red-green colorblindness is a genetic condition that affects your ability to see certain colors. In some cases, red-green colorblind people see only green and brown as different. Others can’t tell reds and oranges apart or yellows and greens.
The reason people have red-green colorblindness is that the cells in their eyes that should detect red light don’t work. This means they don’t see reds like people with normal vision do. They either don’t see them at all or see them as something else, like oranges or browns.
Colorblindness can affect one eye or both eyes. This is called dichromacy. It depends on which cones aren’t working.
Red-Green Color Vision Deficiency – More Common Than You Know
Red-green colorblindness is the most common form of colorblindness in men, affecting 7 percent of all men. It’s rare in women, though, affecting only 0.4 percent of all women.
The number of people who are colorblind is estimated to be around 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women. However, there are no reliable figures on how many people are affected by red-green color blindness.
Top10 population of Red Green Colorblind People in Countries
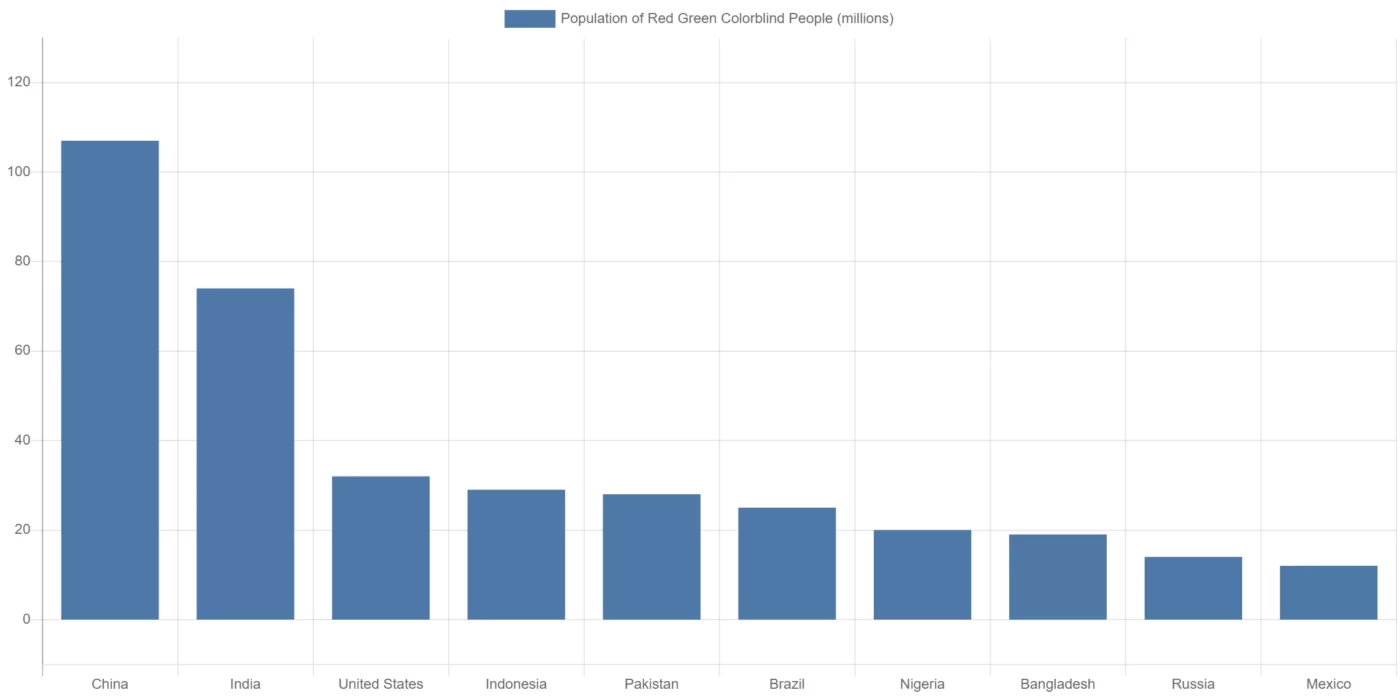
- China:107 million
- India: 74 million
- United State:32 million
- Indonesia:29 million
- Pakistan: 28 million
- Brazil: 25 million
- Nigeria: 20 million
- Bangladesh: 19 million
- Russia:14 million
- Mexico: 12 million
Genetic Factors: Is Color Blindness Hereditary?
Red Green Color Blindness Is An X Linked Recessive Disorder
Red-green colorblindness is due to an abnormal gene on the X chromosome. Men have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome while women have two X chromosomes. If a man inherits two bad copies of the gene, he will be colorblind. But, a woman will get only one bad copy. Her other copy may compensate for it. If both men and women are color blind, they will be equally affected.
It is inherited and can be passed down from either parent.
If both parents have red-green colorblindness, there’s a 25 percent chance their child will be affected. If only one parent has red-green colorblindness, there’s a 50 percent chance their child will be affected. But if neither parent has red-green colorblindness, there’s no risk that their child will have it.
Trauma or injury to the eye, optic nerve, or brain can also cause color blindness. So can AMD.
AMD affects central vision. It causes loss of pigmentation in the macula at the back of your eye’s retina. The macula is where light-sensing cells (photoreceptors) are.
How To Diagnose?
There are several tests that doctors use to test red green color blindness. Some are simple. Others need special equipment, like an eye exam with a machine called an anomaloscope. It measures how well a person can tell between two similar colors.
The Ishihara Test
The Ishihara color vision test is a common test used to identify red-green color blindness. It uses a series of circles containing numbers that are printed in different colors. The patient is asked to identify the numbers.
The following image shows an example of the test:
Test your eye is or not have color blindness
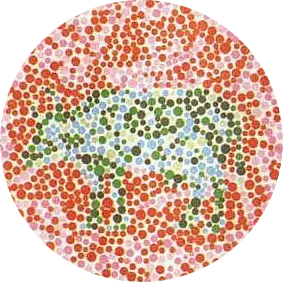
Average Person: Cow
Red Green Color Blindness: Deer

Average Person: 26
Red Color Blindness: 6
Green Color Blindness: 2
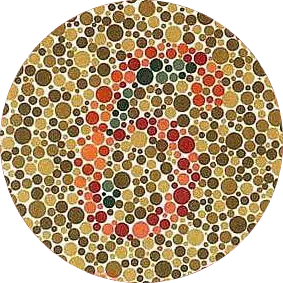
Average Person: 6
Red Green Color Blindness: 5
Full Color Weakness: NO ANY
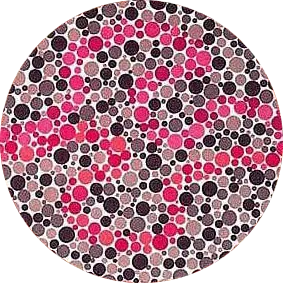
Average Person: Purple Line and Red Line
Red Color Blindness: Purple Line
Green Color Blindness: Red Line

Average Person: No ANY
Red Green Color Weakness: Curve Line
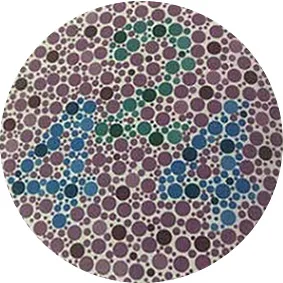
Average Person: 424
Red Color Blindness: 2
Green Color Blindness: 44
The Anomaloscope

The Anomaloscope is a device that uses light and a filter to split colors. This shows you which wavelengths your eye absorbs. A color-blind individual will absorb more light than they can perceive, while a person with normal vision will absorb less. The Anomaloscope will help you see if you have red/green color blindness. It does this by measuring how much light your eyes absorb.
The test consists of two different lights: one red, and one green (although some models use white light instead and may mix in other colors). Look through the eyepiece at these lights. Wear filters over each eye. One lets in only red light. The other lets in only green. The circles appear black or gray when seen with both filters at once. But, they become colored when seen by themselves with only one filter. This means your retina has some deficiency affecting the perception of reds or greens (or both).
Color Matching
If you have a color blindness test, it’s likely that the test will use a special color matching chart. This is the best way to test for red-green colorblindness. It requires you to match the colors on your screen to those on a printed chart. The chart has squares of red, green, yellow, and blue.
There are two main types of color matching tests. One uses colored tiles. The other uses colored dots with patterns underneath them. To do this type of test, you need to put each tile or dot into its correct place on either side of a dividing line (or in some cases over another pattern). You should use this information about where each square fits to find the shade of each square. You can call them by their number or letter code (e.g., “square 2A”).
Can Red Green Colorblind Be Cured?
There is no cure for Red Green Colorblindness. If you are colorblind, you have a deficit in the cone cells of your retina, which are responsible for color vision. These cells can’t see some types of light as they should. So, they can’t transmit information to the brain. This is why people with red-green colorblindness often confuse green and brown or blue and gray.
The only way to cure red-green colorblindness is to replace damaged cone cells with healthy ones. But, there hasn’t been much research in this field. This is because of ethical concerns about stem cells.
Life Through the Lens: Real Experience of Color Blindness
Treatments for red-green colorblindness exist. They can help people with this condition see colors more clearly. They include glasses, contact lenses.
Colorblind Glasses

If you are colorblind, Color blind glasses might be the most effective treatment for red green colorblindness. Colorblind glasses have a filter that is designed to enhance the colors that are seen by the colorblind person. This can help a person with red-green color blindness see colors. It can help them do everyday tasks more easily.
Colorblind glasses are not for everyone. They are costly and not always covered by insurance or programs like Medicare or Medicaid. However, if you have some money to spend on yourself or someone else who wants better vision. But, they do not want surgery or laser treatment. Then, these may be good options for you!
Colored Contact Lenses For Red Green Colorblind
Colored contact lenses are a surgical option for people with red green color blindness. They work by filtering out the wavelengths that you can’t see, allowing you to see those colors correctly.
How does it work? Colored contacts come in many shades. They filter out some light that your eye can’t detect. This lets you see more clearly. For example, if you have red-green color blindness, wearing blue-tinted contacts could help. They filter out the red or green wavelengths in front of your eyes. This makes them easier for you to tell apart. This means that colours appear brighter, more vibrant and less washed out.
No science proves it yet. But, some studies suggest that colored contacts may also improve contrast sensitivity. This is for people who wear glasses or have low vision conditions like macular degeneration (AMD). Also, some patients report improved vision after wearing colored contacts for months. Others do not notice any difference.
Color Blind Glasses Help You Pass Ishihara Test
What Are Glasses For Color Blindness Red-green?
Red-Green Color Blind Corrective Glasses are lenses. They help people with red-green color blindness see the difference between shades of red and green. These glasses are for people who struggle to tell these two colors apart. They contain special lenses that filter out certain wavelengths of light so that they can be seen more clearly.
How do Red Green Color Blind Glasses Work?
Red-green color blind glasses filter out some light. This makes the light that remains clearer to someone with red-green color blindness. The glasses do one of two things. They either filter out all but the visible wavelengths. Or, they filter out specific wavelengths to help with a particular type of color deficiency (like protanopia).
Color blind glasses, also known as Aniridia glasses, are the most common form of vision correction for those with color blindness. They are made from polycarbonate and are able to filter out certain wavelengths of light. This allows one to see the world in a different way by allowing them to see more clearly than they would otherwise be able to.
Colorblind Glasses Benefits
- Improve Your Daily Life
- Pass Color Blindness Tests
- Correct Colorblindness
- Increase Confidence In Social Situations
- Get The Right Shades For Your Activities
Colorblind Contact lenses Benefits
- Glasses-free Color Correction Solution
- Pass Color Blindness Tests
- Avoid Embarrassment
- A Boost In Confidence
- Look Great In Photos
- Prevent Discrimination
- Better Job Opportunity
Color blindness contacts are an alternative to wearing color blind glasses. They are made of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and can be worn over your regular contact lenses if you already have them. The PMMA acts as a filter that allows you to see the world in a different way by filtering out certain wavelengths of light. This lets you see the world in a clearer light than you would otherwise be able to see it in.
Frequently Asked Questions:
At what age can color blindness be diagnosed?
Color blindness is usually diagnosed at a young age, often when children start learning colors.
Can color blindness affect learning?
It might make certain tasks more challenging, but with proper support, it isn’t a barrier to academic success.
Can someone with color blindness still drive?
Yes, they are still able to drive, however the colours of traffic lights may appear differently to them.
Can color blindness skip a generation?
Yes, it’s possible. The gene that influences red-green color blindness is recessive and carried on the X chromosome, which can be passed down silently.
Can colour blindness be prevented?
Since it’s usually a genetic condition, it can’t be prevented.
Can you suddenly become color blind?
Most color blindness is inherited and present at birth. However, some diseases, conditions, or exposure to certain chemicals can cause color blindness.
Can lifestyle affect color blindness?
Lifestyle doesn’t affect genetic color blindness, but certain lifestyle factors might contribute to acquired color vision problems.
Can people with color blind join the military?
It depends on the severity of the deficiency and the specific branch of the military.
How does color-blindness affect children in school?
It might affect learning activities that rely on color, but most children adjust well with the right support.
Can foods or supplements improve colour blindness?
Foods or supplements cannot correct genetic color blindness.
Conclusion
Learning to live with red-green color blindness can be a daunting task. There are many things such as money, driving, and even people that you thought you knew very well but your red-green colorblindness has changed all of them
What was once simple is now difficult and leaves you with so many questions. Blind dates, holidays, riding bikes, or just coming home from work can cause anxiety due to all the uncertainty.
Color Blind Glasses help red green color blind people open a new world of colors, making it easier to go out, work, travel, and study while avoiding any disturbing situations.
Articles You Might Interest
80 Surprising Facts About Color Blindness
How To Pass the Color Blindness Test
The Latest Research on Achromatopsia and Possible Treatments

